Architecture
Virtual clusters are fully functional Kubernetes clusters nested inside a physical host cluster. These virtual clusters are designed to provide better isolation and flexibility for optimal multi-tenancy.
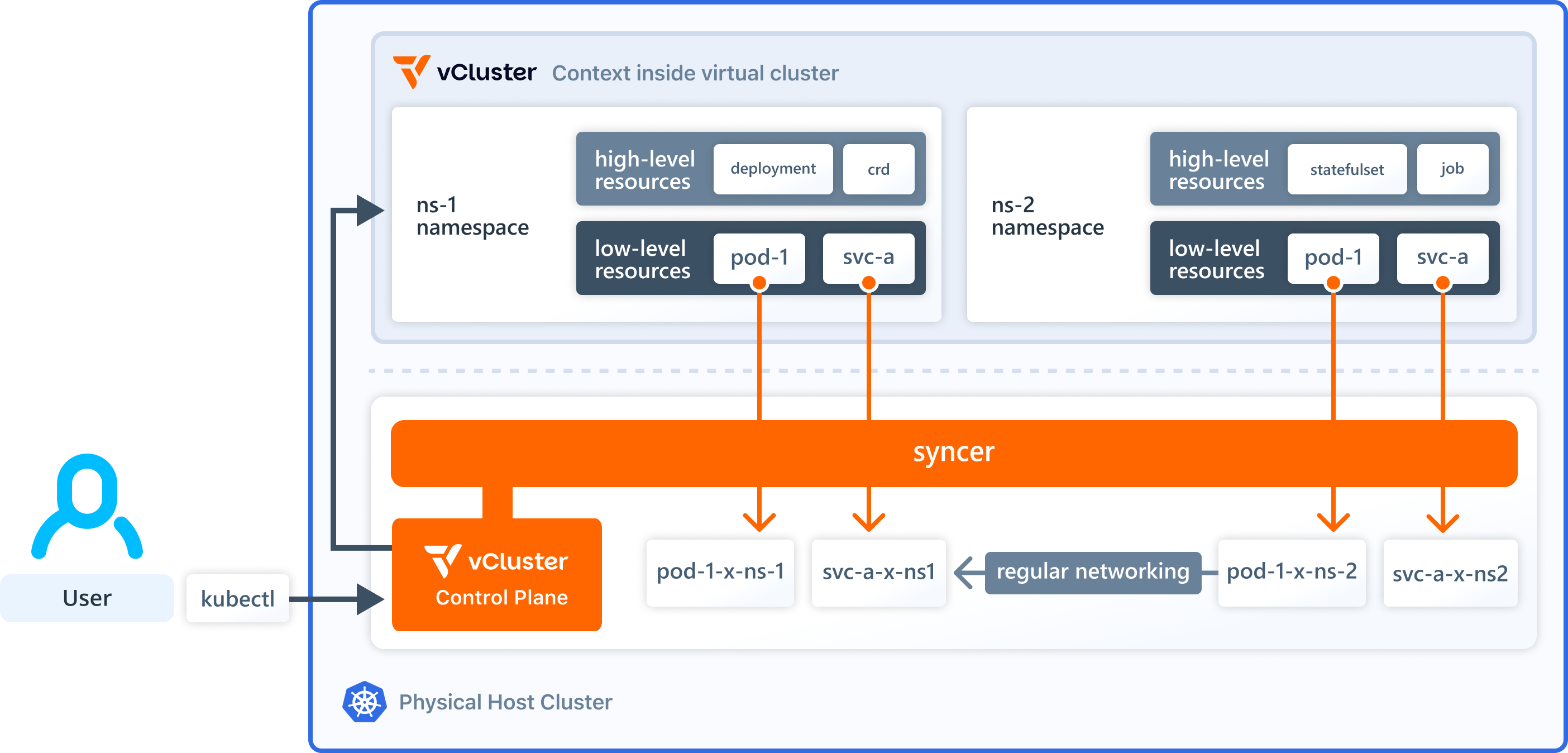
Virtual cluster components
Virtual control plane
vCluster creates isolated Kubernetes environments by deploying a virtual cluster that contains its own dedicated virtual control plane. This control plane orchestrates operations within the virtual cluster and facilitates interaction with the underlying host cluster.
The virtual control plane is deployed as a single pod managed as a StatefulSet (default) or Deployment and it has the following components:
- A Kubernetes API server, which is the management interface for all API requests within the virtual cluster. It supports a variety of Kubernetes distributions, including vanilla Kubernetes (default), Lightweight Kubernetes (K3s), and Zero Friction Kubernetes (k0s).
- A controller manager, which maintains the state of Kubernetes resources like pods, ensuring they match the desired configurations.
- A data store, which is a connection to or mount of the data store where the API stores all resources. By default, an embedded SQLite is used as the datastore, but you can choose other data stores like etcd, MySQL, and PostgreSQL.
- A syncer, which is a component that synchronizes resources to and from the virtual cluster and host cluster and facilitates workload management on the host's infrastructure.
- A scheduler, which is an optional component that schedules workloads. By default, vCluster reuses the host cluster scheduler to save on computing resources. If you need to add node labels or taints to control scheduling, drain nodes, or utilize custom schedulers, you can enable the virtual scheduler.
Syncer
A virtual cluster doesn't have actual worker nodes or a network. Instead, it uses a syncer component to synchronize the virtual cluster pods to the underlying host cluster. The host cluster schedules the pod, and the syncer keeps the virtual cluster pod and host cluster pod in sync.
Higher-level Kubernetes resources, such as Deployment, StatefulSet, and CRDs only exist inside the virtual cluster and never reach the API server or data store of the host cluster.
By default, the syncer component synchronizes certain low-level virtual cluster Pod resources, such as ConfigMap and Secret, to the host namespace so that the host cluster scheduler can schedule these pods with access to these resources.
While primarily focused on syncing from the virtual cluster to the host cluster, the syncer also propagates certain changes made in the host cluster back into the virtual cluster. This bi-directional syncing ensures that the virtual cluster remains up-to-date with the underlying infrastructure it depends on.
You can configure what and how the syncer synchronizes to and from the host cluster depending on your use case.
Host cluster and namespace
Each virtual cluster runs as a regular StatefulSet (default) or Deployment inside a host cluster namespace. Everything that you create inside the virtual cluster lives either inside the virtual cluster itself and/or inside the host namespace.
It is possible to run multiple virtual clusters inside the same namespace. You can even run a virtual cluster inside another virtual cluster, otherwise known as vCluster nesting.
For certain cases that don't require strong isolation, you can run workloads in multiple underlying host namespaces. However, this feature is experimental and requires more management overhead.
Networking in virtual clusters
Networking within virtual clusters is crucial for facilitating communication within the virtual environment itself, across different virtual clusters, and between the virtual and host clusters.
Ingress traffic
Instead of having to run a separate ingress controller in each virtual cluster to provide external access to services within the virtual cluster, vCluster can synchronize Ingress resources to utilize the host cluster's ingress controller, facilitating resource sharing across virtual clusters and easing management like configuring DNS for each virtual cluster.
DNS in virtual clusters
By default, each virtual cluster deploys its own individual DNS service, which is CoreDNS. The DNS service lets pods within the virtual cluster resolve the IP addresses of other services running in the same virtual environment. This capability is anchored by the syncer component, which maps service DNS names within the virtual cluster to their corresponding IP addresses in the host cluster, adhering to Kubernetes' DNS naming conventions.
With vCluster Pro, CoreDNS can be embedded directly into the virtual control plane pod, minimizing the overall footprint of each virtual cluster.
Communication within a virtual cluster
Pod to pod
Pods within a virtual cluster communicate using the host cluster's network infrastructure, with no additional configuration required. The syncer component ensures these pods maintain Kubernetes-standard networking.
Pod to service
Services within a virtual cluster are synchronized to allow pod communication, leveraging the virtual cluster's CoreDNS for intuitive domain name mappings, as in regular Kubernetes environments.
Pod to host cluster service
Services from the host cluster can be replicated into the virtual cluster, allowing pods within the virtual cluster to access host services using names that are meaningful within the virtual context.
Pod to another virtual cluster service
Services can also be mapped between different virtual clusters. This is achieved through DNS configurations that direct service requests from one virtual cluster to another.
Communication from the host cluster
Host pod to virtual cluster service
Host cluster pods can access services within a virtual cluster by replicating virtual cluster services to any host cluster namespace. This enables applications running inside the virtual cluster to be accessible to other workloads on the host cluster.